Dichotomous Key Definition
A dichotomous key is a widely used tool in biology and other sciences to identify and classify organisms or objects based on observable characteristics. It works through a series of two-part choices. These choices can be based on qualitative traits (like color or shape) or quantitative traits (like number of legs or height), and the key can be presented in written or graphical (flowchart) form.
Dichotomous keys are especially useful for identifying plants, animals, and microorganisms, and are commonly used by both students and professionals. The term “dichotomous” means “divided into two parts,” reflecting the format of contrasting pairs of statements used at each decision point.
How to Make Dichotomous Key
Step 1: List down the characteristics
Pay attention to the specimens you are trying to identify with your dichotomous key using a dichotomous key maker . List down the characteristics that you can notice. For example, say you are trying to classify a group of animals. You may notice that some have feathers whereas others have legs, or some have long tails and others don’t.
Step 2: Organize the characteristics in order
When creating your dichotomous key, you need to start with the most general characteristics first, before moving to the more specific ones. So it helps to have identified the more obvious and less obvious contrasting characteristics among the specimen before creating your dichotomous key.
Step 3: Divide the specimens
You can use statements (i.e. has feathers and no feathers) or questions (does it have feathers?) to divide your specimens into two groups. The first differentiation should be made on the most general characteristic.
Step 4: Divide the specimen even further
Based on the next contrasting characteristic, divide the specimen further. For example, first, you may have grouped your animals as having feathers and have no feathers, in which case the ones with feathers can be categorized as birds while you can further subdivide the ones that have no feathers as having fur and having no fur. Continue to subdivide your specimen by asking enough questions until you have identified and named all of them.
Step 5: Draw a dichotomous key diagram
You can either create a text-based dichotomous key or a graphical dichotomous key maker where you can even use images of the specimen you are trying to identify.
Step 6: Test it out
Once you have completed your dichotomous key, test it out to see if it works. Focus on the specimen you are trying to identify and go through the questions in your dichotomous tree to see if you get it identified at the end. If you think the questions in your dichotomous key need to be rearranged, make the necessary adjustments.
Helpful Resources
Visually organize large amounts of information to quickly identify, categorize, and analyze organisms.
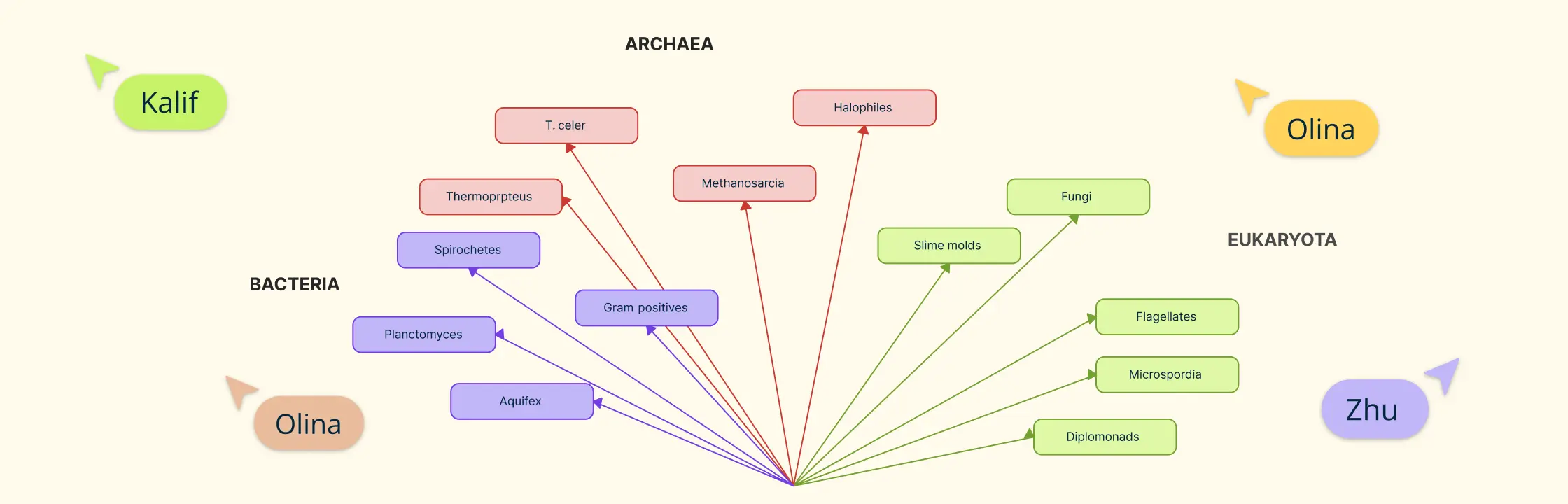
Effectively visualize and identify the evolutionary relationships among various biological species.
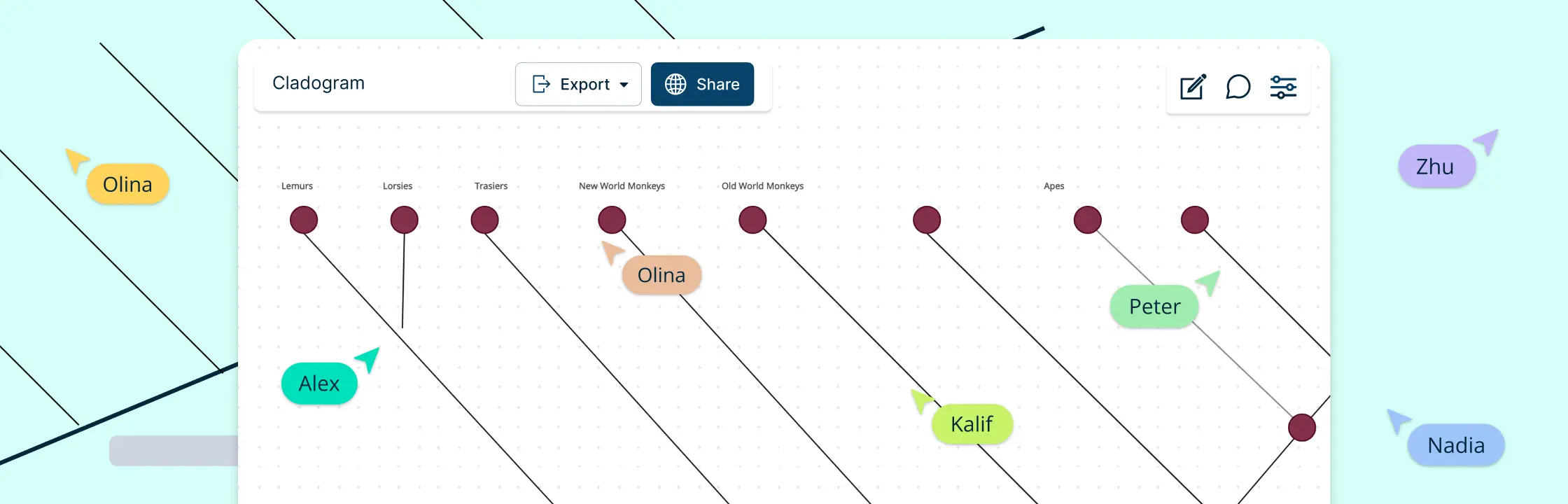
Effectively visualize and identify the phylogenetic relationships among various biological species with cladograms.
Key Features of Creately’s Dichotomous Key Maker:
- User-Friendly Interface: Easily drag and drop elements to build logical flows for species classification or any binary decision-making process.
- Customizable Templates: Choose from a variety of pre-designed templates and shapes to create professional-looking dichotomous keys quickly.
- Real-Time Collaboration: Work together with peers and colleagues simultaneously, making group projects and classroom activities more interactive.
- Flexible Export Options: Save your work in multiple formats such as PNG, JPEG, SVG, and PDF for hassle-free sharing, printing, and publishing.
- Versatile Applications: Ideal for both basic educational purposes and advanced scientific research, Creately helps streamline the process of identifying and categorizing organisms.
- Evolutionary Connection Tools: To draw connections between species and better establish evolutionary relationships, use our Phylogenetic Tree Maker or Online Cladogram Maker.
Free Dichotomous Key Examples
Resources:
LibreTexts Website LibreTexts. (n.d.) Introduction to Dichotomous Keys. In: Red Seal Landscape Horticulturist: Identify Plants and Plant Requirements I (Nakano). Available at: https://bio.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Agriculture_and_Horticulture
PDF from Texas A&M Texas A&M University. (n.d.) Dichotomous Key Activity [PDF]. Available at: https://tfsweb.tamu.edu/uploadedFiles/TFSMain/Learn_and_Explore/Conservation_Education_Resources