Swimlane diagrams are a visual tool that breaks down tasks by roles or departments, helping everyone involved understand their responsibilities and how they fit into the larger process. In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about swimlane diagrams—from understanding their key components to learning how to create and use them effectively. Whether you’re new to process mapping or looking for a way to improve your workflow management, this guide will provide practical tips and examples to get you started.
What Is a Swimlane Diagram
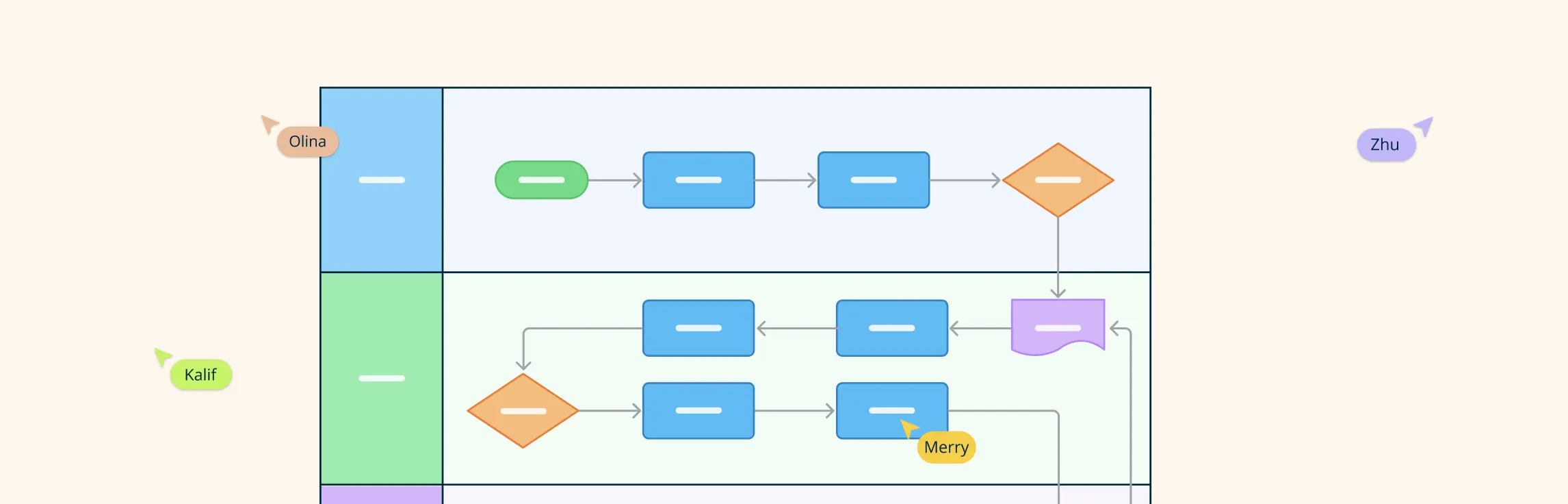
A swimlane diagram is a type of flowchart that organizes a process by dividing it into different “lanes,” each representing a specific role, team, or department. The tasks or steps in the process are placed in these lanes, showing who is responsible for each part of the workflow. This simple visual structure makes it easy to understand how tasks flow from one person or team to the next, highlighting who is doing what at each stage of the process.
Swimlane diagrams are valuable for clarifying roles and responsibilities within a process, making it easier to spot inefficiencies, delays, or bottlenecks. They help improve communication by providing a shared visual reference that keeps everyone aligned on their tasks. This is particularly useful in complex processes, where it can be difficult to track who’s handling each step. Creating a swimlane diagram helps clarify where each task belongs, which helps reduce confusion and ensure smoother operations.
Industries and scenarios where swimlane diagrams are most useful
These diagrams are used across various industries and scenarios. In project management, they help visualize and track tasks across teams, while in healthcare, they can map out patient care processes and department workflows. For software development, they outline the lifecycle from planning to deployment, ensuring tasks are handled by the right team.
Customer service teams use them to show how different departments interact with customers, improving efficiency and service. Similarly, in manufacturing and marketing, swimlane diagrams help map production processes or campaign workflows, ensuring that everyone knows their responsibilities and the process stays on track. Overall, swimlane diagrams are a versatile tool for improving process management, communication, and efficiency in any industry.
History of Swimlane Diagrams
Swimlane diagrams originated in the mid-20th century as part of process improvement techniques. They evolved from traditional flowcharts to better visualize workflows involving multiple roles or departments.
- 1940s-1950s: Businesses adopted more structured methods to visualize processes. The concept of dividing tasks into “lanes” was introduced to assign clear responsibilities.
- Term “Swimlane”: The name comes from the resemblance to lanes in a swimming pool, with each lane representing a specific role, team, or department.
- Early Use: Initially popular in industries like manufacturing and operations, where cross-functional collaboration and task ownership were essential.
- Growth and Adoption: As businesses grew more complex and technology advanced, swimlane diagrams became widely used across various industries, including healthcare and software development.
- Today: They are a key tool for mapping workflows, improving communication, and identifying inefficiencies by clearly showing who is responsible for each task.
The evolution of swimlane diagrams reflects the need for clear, simple tools to manage complex systems and processes.
Types of Swimlane Diagrams
Swimlane diagrams come in different types depending on how they are organized and what they are used for. Here are the main types:
1. Horizontal swimlane diagram
In this type, the lanes are arranged horizontally across the diagram, like rows. Each row represents a role, team, or department involved in the process. Horizontal swimlane diagrams are the most common format and are ideal for showing a step-by-step process where tasks flow from left to right.
2. Vertical swimlane diagram
Here, the lanes are arranged vertically, like columns. Each column represents a role, team, or department. Vertical swimlane diagrams are often used when processes flow from top to bottom, making them useful for hierarchical workflows or decision-making processes.
3. Cross-functional swimlane diagram
This type is specifically designed for processes that involve multiple teams or departments working together. It clearly shows how tasks move across functions, making it easier to identify handoffs, delays, or bottlenecks in cross-functional workflows.
4. Flowchart with swimlanes
This is a combination of a traditional flowchart and a swimlane diagram. It includes detailed steps with arrows, decision points, and symbols within the lanes, providing a highly detailed map of a process while still highlighting roles and responsibilities.
5. Specialized swimlane diagrams
These are tailored for specific industries or purposes. For example:
- IT processes: Swimlane diagrams for software development or IT workflows often include stages like planning, development, testing, and deployment.
- Healthcare: Swimlane diagrams can map patient care processes, showing roles like doctors, nurses, and administrative staff.
- Marketing: Campaign planning swimlanes break down tasks between design, content creation, and approvals.
When to Use Swimlane Diagrams
Swimlane diagrams are best used when you need to organize and clarify processes that involve multiple roles, teams, or departments. Here are some situations where they can be especially helpful:
Visualizing complex workflows
When a process has many steps and involves multiple people or teams, it can quickly become hard to follow. Swimlane diagrams help break down these complexities by organizing tasks into clear lanes, making it easier to understand the overall flow of work.
Assigning roles and responsibilities
If you need to clearly define who is responsible for each step in a process, a swimlane diagram is ideal. It shows at a glance which role or team owns each task, helping to eliminate confusion and ensure accountability.
Identifying inefficiencies or bottlenecks
Swimlane diagrams are great for spotting problem areas in workflows. For example, they can highlight delays during handoffs between teams or reveal steps that may be unnecessary. This makes them useful tools for improving efficiency.
Coordinating cross-functional teams
When teams from different departments or functions need to work together, swimlane diagrams can improve collaboration by showing how tasks are shared and where responsibilities overlap. This ensures smoother communication and reduces misunderstandings.
Explaining or documenting processes
Swimlane diagrams are perfect for explaining a process to others, whether you’re onboarding new team members or presenting workflows to stakeholders. Their clear structure makes it easy for anyone to understand the sequence of tasks and roles involved.
Supporting process improvement initiatives
If you’re working on optimizing a workflow, swimlane diagrams can help you visualize the current process and identify areas for improvement. They provide a clear baseline to compare against future changes.
Managing projects and workflows
Project managers often use swimlane diagrams to map out tasks, deadlines, and team responsibilities. This helps keep everyone aligned and ensures the project stays on track.
How to Create a Swimlane Diagram in 5 Simple Steps
ting a swimlane diagram involves several key steps, each of which helps you build a clear and effective visual representation of a process. Let’s explore these steps in detail:
1. Define the purpose
Start by identifying why you’re creating the swimlane diagram. Is it to improve a workflow, clarify roles, or identify bottlenecks? Having a clear purpose ensures the diagram focuses on the right aspects of the process. For example, if the goal is to streamline a customer service workflow, your diagram should highlight handoffs between teams and areas of potential delays.
Once you’ve defined the purpose, set specific objectives. Ask yourself:
- What do I want this diagram to achieve?
- Who will use it, and how will it help them?
This clarity helps you decide how detailed the diagram needs to be and what information to include.
2. Identify lanes and assign roles
Next, determine the participants or teams involved in the process. Each participant gets their own lane in the diagram. Think of these lanes as containers that show what tasks belong to whom.
For example:
- In a marketing workflow, you might have lanes for design, content creation, approvals, and publishing.
- In a software development process, lanes could represent teams like developers, QA testers, and project managers.
Label each lane clearly so that everyone looking at the diagram knows who is responsible for which part of the process.
3. List tasks or steps
Break the process into individual tasks or steps. Start from the beginning and identify each action needed to complete the process. It helps to focus on manageable actions rather than overly broad steps.
For instance:
- In a hiring process, steps might include posting the job, screening resumes, conducting interviews, and sending offers.
- Be specific: Instead of “interview candidate,” you could use “schedule interview,” “conduct interview,” and “provide feedback.”
This detailed breakdown ensures no part of the process is overlooked.
4. Arrange and connect tasks within lanes
Now, place each task in the appropriate lane based on who is responsible for it. Arrange the tasks in the order they happen, showing the flow of the process.
Use arrows or lines to connect the tasks, indicating the sequence and direction of the workflow. Include decision points, if any, to show where choices are made that affect the process. For example:
- “Approve design?” could lead to two different outcomes: one arrow for “Yes” (proceed to the next step) and another for “No” (return to revisions).
This arrangement not only shows the workflow but also highlights how different roles interact and where tasks are handed off.
5. Validate and refine
Once your diagram is complete, review it carefully for accuracy and clarity. Share it with others involved in the process, such as team members or stakeholders, to get their feedback.
Check for:
- Accuracy: Does the diagram reflect the process as it actually happens?
- Completeness: Have you included all steps, roles, and connections?
- Clarity: Is the diagram easy to understand?
Refine the diagram based on feedback, simplifying where needed or adding details if certain parts are unclear. A validated and polished swimlane diagram ensures it serves its purpose effectively.
Who Uses Swimlane Diagrams?
Swimlane diagrams are versatile and can be used by anyone managing or analyzing processes. Here are some key groups that benefit from them:
- Project managers: To plan and track project workflows, assign tasks, and monitor progress across teams.
- Business analysts: To visualize and improve processes by identifying inefficiencies or bottlenecks.
- Team leaders: To clearly define responsibilities and ensure smooth collaboration between departments.
- Operations managers: To map workflows in manufacturing, logistics, or other operational areas for better efficiency.
- Software developers and IT professionals: To document processes like software development lifecycles, system designs, or IT workflows.
- HR professionals: To outline recruitment, onboarding, or performance review processes.
- Educators and trainers: To design and explain teaching plans or training workflows.
Swimlane diagrams are adaptable tools that work well for any process involving multiple roles or teams, making them valuable across industries and professions.
Key Components of Swimlane Diagrams
A swimlane diagram is made up of several key components that help organize and clarify a process.
Lanes
Lanes are one of the most important features of a swimlane diagram. Each lane represents a specific role, team, or department involved in the process. These lanes can be arranged horizontally or vertically, and each one is assigned a set of tasks or actions that the corresponding team or person is responsible for. The purpose of lanes is to show who is doing what at each step of the process, making it easy to understand how tasks flow between different roles.
Processes or tasks
Processes or tasks are the actions that take place within the workflow. These are depicted as steps or boxes inside the lanes. Each box represents a task or action that needs to be completed, and it’s placed in the lane of the team or individual responsible for it. The tasks are connected in a sequence, showing the order in which they need to happen.
Flow connectors
Flow connectors are arrows or lines used to connect the tasks and show how they flow from one to the next. These connectors help guide the viewer through the process, showing the direction and order of tasks. Arrows are the most common type of flow connector, indicating the movement of work from one step to the next. Other symbols, like diamonds for decision points, can also be used to indicate when choices need to be made.
Roles or entities
Roles or entities are the people or groups responsible for carrying out each task. These are often represented by the lanes themselves, but can also be listed within the diagram to clarify exactly who is in charge of what. Assigning roles is essential for ensuring everyone knows their responsibilities and understands how they fit into the overall process.
Benefits of Swimlane Diagrams
Swimlane diagrams are more than just visual tools—they are powerful aids for improving processes, communication, and efficiency. Here are the key benefits they offer:
1. Clear roles and responsibilities
Swimlane diagrams make it easy to see who is responsible for each part of a process. By dividing tasks into lanes assigned to specific roles or teams, there’s no confusion about ownership. Everyone can quickly understand their responsibilities and how their work fits into the bigger picture.
2. Improved process clarity
By visually mapping out tasks and showing how they connect, swimlane diagrams simplify even the most complex workflows. They clearly show the sequence of actions, handoffs between roles, and decision points, making it easier to spot inefficiencies or gaps in the process.
3. Enhanced collaboration
When teams or departments work together, misunderstandings can arise about who does what. A swimlane diagram acts as a shared reference point, helping everyone stay aligned and reducing miscommunication. This is especially useful for cross-functional projects where multiple teams need to coordinate efforts.
4. Identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies
Swimlane diagrams help pinpoint problem areas in a workflow. For example, if one lane has too many tasks or delays occur at specific handoff points, you can easily identify these bottlenecks and take corrective action. This makes processes more efficient and reduces wasted time and resources.
5. Easier process improvement
When you can see the entire workflow in one visual, it’s easier to analyze and improve it. Swimlane diagrams help you spot unnecessary steps, streamline handoffs, and optimize resource allocation. They are invaluable tools for continuous process improvement.
6. Effective training and communication
Swimlane diagrams are excellent for employee onboarding or explaining processes to stakeholders. Their clear, structured format makes it easier for people to understand workflows without needing lengthy explanations. This boosts understanding and speeds up training.
7. Adaptable across industries
Whether it’s project management, healthcare, marketing, software development, or manufacturing, swimlane diagrams can be tailored to suit any industry. Their versatility makes them an essential tool for visualizing workflows and improving processes in a wide range of scenarios.
Swimlane Diagrams vs Flowcharts
Swimlane diagrams and flowcharts are both tools for visualizing processes, but they serve different purposes and have unique strengths. Here’s a simple comparison to help you understand the differences:
1. Purpose
- Flowcharts are ideal for mapping out the sequence of steps in a process. They focus on what happens and in what order, making them great for basic workflows or decision-making paths.
- Swimlane diagrams add another layer by showing who is responsible for each step. They organize tasks into lanes based on roles, teams, or departments, making them better suited for processes involving multiple participants.
2. Focus
- Flowcharts focus on the flow of tasks or decisions. They are straightforward and emphasize the steps in a process.
- Swimlane diagrams focus on both the flow of tasks and the accountability of roles. They highlight how different participants interact and where handoffs occur.
3. Visual structure
- Flowcharts are simpler and typically use shapes like rectangles, diamonds, and arrows to show the flow of tasks.
- Swimlane diagrams are divided into horizontal or vertical lanes, each representing a role or entity. Tasks are placed within these lanes, providing a structured view of responsibilities.
4. Use cases
- Flowcharts are best for:
- Visualizing a straightforward process.
- Mapping decision points, like “yes/no” paths.
- Explaining a process step-by-step for training or documentation.
- Swimlane diagrams are best for:
- Processes with multiple roles or teams involved.
- Cross-functional workflows where handoffs need to be clear.
- Identifying inefficiencies, delays, or role overlaps in complex processes.
5. Complexity
- Flowcharts are simpler and quicker to create, but they lack the ability to show who does what.
- Swimlane diagrams are slightly more complex but provide deeper insights by combining task flow and role clarity.
Swimlane Diagram Examples
In this section, we’ll look at some swimlane diagram examples to show how they can be used in different real-world processes. These examples will help you see how swimlane diagrams simplify workflows and clarify roles.
Support Process Swimlane Template
Swimlane for Fast Food Order
BPMN Swimlane Diagram Template
BPMN Swimlane Diagram Template
Verticle Swimlane Diagram Template
Common Swimlane Diagram Mistakes
Swimlane diagrams are powerful tools for organizing processes, but certain mistakes can make them confusing or less effective. Here are some common errors to watch out for and how to avoid them:
1. Overloading the diagram with too much detail
Including every single step or task can make the diagram overwhelming and hard to follow. Instead, focus on key steps that are essential to understanding the process. Keep it clear and concise, and use supporting documents or notes for extra details if needed.
2. Misaligned lanes or tasks
Poor alignment of lanes or misplaced tasks can create confusion about roles and responsibilities. Ensure that each task is placed in the correct lane and that the lanes are clearly labeled. Using tools like Creately, which offers auto-alignment features, can help maintain a neat and professional look.
3. Missing or unclear flow connectors
Arrows and lines are critical for showing the sequence of tasks and how they connect. If they’re missing, ambiguous, or crossed unnecessarily, it can confuse viewers. Always use clear, directional flow connectors and avoid clutter by minimizing overlapping lines.
4. Failing to define roles or entities properly
If the roles or teams represented by the lanes are not clearly defined, it becomes difficult to understand who is responsible for what. Use specific and descriptive labels for each lane, such as “HR Team” or “Finance Department,” instead of vague terms like “Team 1.”
5. Ignoring decision points
Processes often include decision-making steps, but leaving these out can make the diagram incomplete. Use decision shapes (like diamonds) to show points where choices are made, and include clear paths for each possible outcome.
6. Overcomplicating with unnecessary lanes
Adding too many lanes can clutter the diagram and dilute its purpose. Stick to the participants or roles directly involved in the process and group related tasks under the same lane if appropriate.
7. Not validating the diagram
If the swimlane diagram doesn’t reflect the actual process, it won’t be useful. Always review it with the people involved in the workflow to ensure accuracy. Validation helps identify errors, gaps, or steps that might have been missed.
8. Skipping updates for changing processes
Processes evolve over time, and outdated diagrams can lead to confusion. Make it a practice to review and update swimlane diagrams regularly to keep them relevant. Tools like Creately, with centralized modeling capabilities, make this easier by reflecting updates across all connected diagrams.
Helpful Resources
Learn the essentials of process mapping with our comprehensive guide. Discover techniques, best practices, and tools to streamline workflows and improve efficiency.
Explore various business process modeling techniques with real-world examples. Learn how to visualize, analyze, and improve workflows for greater efficiency and clarity.
Create organized and efficient swimlane diagrams with Creately's intuitive software. Explore customizable templates, real-time collaboration, and seamless integration to streamline your workflows and enhance team productivity.
Best Practices for Creating Swimlane Diagrams
Creating effective swimlane diagrams requires careful planning and attention to detail. Following these best practices will help you create clear, accurate, and easy-to-understand diagrams:
1. Keep it simple and focused
Don’t overwhelm the diagram with too many details. Focus on the main steps in the process, keeping it clear and concise. If additional information is needed, add notes or reference documents instead of cluttering the diagram.
2. Clearly define lanes and roles
Each lane should represent a specific role, department, or team. Label lanes clearly with descriptive names (e.g., “Marketing Team,” “HR Department”) to avoid confusion. Ensure that everyone understands who is responsible for each task.
3. Use standard shapes and symbols
Stick to standard flowchart shapes for consistency and clarity. For example, rectangles for tasks, diamonds for decision points, and arrows for the flow of the process. This makes it easier for others to interpret the diagram quickly.
4. Keep the flow logical and sequential
Arrange the tasks in a logical order from left to right (for horizontal diagrams) or top to bottom (for vertical diagrams). Make sure the flow is easy to follow and that there’s a clear direction to the process. Avoid unnecessary loops or interruptions.
5. Limit the number of lanes
Too many lanes can make the diagram look cluttered and confusing. Only include the key roles or teams involved in the process. If too many participants are involved, group related roles together under a single lane when possible.
6. Label decision points clearly
Decision points are crucial in most processes. Use diamonds to indicate decisions and label the outcomes clearly (e.g., “Yes” or “No”) to show the different paths the process might take.
7. Use color and formatting sparingly
Color can be useful for highlighting key information, but avoid overusing it. Stick to a simple color scheme that enhances readability without distracting from the content. Consistent formatting helps create a professional and easy-to-read diagram.
8. Regularly review and update
Processes change over time, so it’s important to keep your swimlane diagram up to date. Regularly review and update it to reflect any changes in roles, tasks, or sequence. Using tools like Creately can help, as updates made in one place can automatically reflect across all connected diagrams.
9. Get feedback from stakeholders
Before finalizing your swimlane diagram, share it with the people who are directly involved in the process. They can provide feedback on its accuracy, clarity, and completeness. This ensures that the diagram truly reflects how the process works.
10. Make it collaborative
If you’re working with a team, make use of collaboration tools that allow others to contribute, comment, or suggest changes in real-time. This ensures everyone is aligned and helps create a more accurate diagram.
Simplify Creating Swimlane Diagrams with Creately
Creating swimlane diagrams is easy and efficient with Creately. Its intuitive features are designed to save time and simplify the process, whether you’re mapping a basic workflow or a complex cross-functional process. Here’s how Creately makes it effortless:
if the new video on swimlanes is approved, pls include it here in the body or on the guide in the helpful resources section.
Easy-to-use templates
Creately offers ready-made swimlane diagram templates that you can customize to suit your needs. You don’t have to start from scratch—simply pick a template, and edit the lanes, tasks, and roles to match your process.
Drag-and-drop interface
The drag-and-drop interface allows you to add and organize lanes, shapes, and connectors with just a few clicks. Moving elements around is smooth and intuitive, making it easy to adjust your diagram as your process evolves.
Automatic alignment and spacing
With Creately, you don’t need to worry about aligning shapes or keeping your diagram neat. It automatically aligns and spaces elements, ensuring your swimlane diagram looks professional and easy to follow.
Collaboration features
Creately makes teamwork seamless. Invite your team to collaborate in real time, so everyone can contribute to the diagram. Add comments, suggest changes, or work together to refine the process—all in one place.
Smart connectors
Adding arrows and lines to show the flow of tasks is quick and hassle-free. Creately’s smart connectors snap into place and adjust automatically when you rearrange elements, saving you time and effort.
Notes and attachments
Add details to your swimlane diagram by attaching documents, images, or notes. This is helpful for providing extra context or linking to resources without cluttering the diagram itself.
Export and share options
Once your swimlane diagram is complete, you can export it in various formats or share it directly with others. Whether it’s for a presentation, training, or collaboration, sharing is simple and flexible.
Centralized modeling for long-term process management
Creately’s advanced modeling capabilities take process mapping to the next level. With its central database for business process models, you can ensure that all your diagrams stay consistent and up-to-date. When you update a process in one diagram, the changes automatically reflect across all connected diagrams and views.
This feature is perfect for long-term process management, allowing you to reuse and adapt processes across multiple workflows without recreating them from scratch. It’s a game-changer for maintaining accuracy, consistency, and efficiency in serious process mapping exercises.
AI assistance with Creately VIZ
Creately’s AI feature, Creately VIZ, can suggest layouts, auto-complete tasks, or optimize your diagram based on your inputs. This speeds up the process and helps you create accurate diagrams effortlessly.
Wrapping Up: The Power of Swimlane Diagrams in Process Management
Swimlane diagrams are powerful tools for visualizing processes, especially when multiple roles or teams are involved. They help clarify the flow of tasks, assign responsibilities, and make complex workflows easier to understand. By organizing tasks into distinct lanes, you can clearly show how different participants interact within the process and where handoffs occur.
To make the most of swimlane diagrams, it’s important to follow best practices—keep the diagram simple, define roles clearly, and ensure the flow is logical. Regularly review and update your diagrams to reflect changes, and always get feedback from stakeholders to ensure accuracy.
With their ability to improve communication, highlight inefficiencies, and aid in process optimization, swimlane diagrams are an invaluable tool for managing and improving workflows. Whether you’re documenting processes for training, problem-solving, or planning, they provide a clear, structured way to view the bigger picture.
References
Validation and Swimlane (2014). Journal of Information Technology Management A Publication of the Association of Management VALIDATION OF BUSINESS PROCESS MODELS USING SWIMLANE DIAGRAMS. DIAGRAMS Journal of Information Technology Management, [online] XXV(4). Available at: https://jitm.ubalt.edu/XXV-4/article3.pdf.
The most common symbols in swimlane diagrams are:FAQs on Swimlane Diagrams
What are the symbols in a swimlane diagram?
Can I use swimlane diagrams for any type of process?
How can swimlane diagrams help in process improvement?
How detailed should a swimlane diagram be?
How can swimlane diagrams improve process efficiency?
Can swimlane diagrams be created without any software?