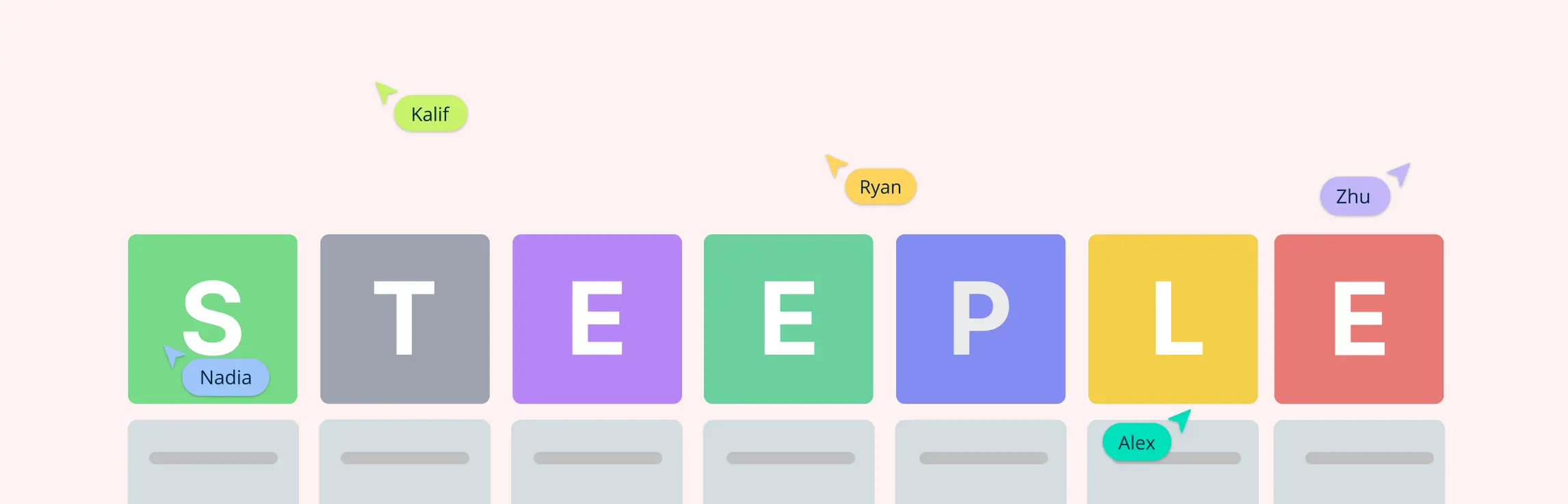
Businesses today must navigate a complex landscape influenced by continuous external changes. Embracing a proactive approach to strategic planning, the STEEPLE analysis emerges as an invaluable tool, providing a comprehensive framework for evaluating external factors impacting business operations. The analysis extends beyond traditional strategies by incorporating social, technological, economic, environmental, political, legal, and ethical factors, giving companies a full spectrum view of their operating environment.
Understanding the importance of these influences is paramount, as they are crucial in shaping business strategies that are both competitive and sustainable. By integrating these external factors into decision-making processes, organizations can align their objectives with broader societal expectations, ensuring that they remain relevant and adaptive in a fast-paced world.
By utilizing tools like the STEEPLE analysis template, businesses can accomplish their targets efficiently through structured analysis frameworks. The integration of contemporary insights allows businesses to optimize strategic approaches further, reinforcing their place in a competitive market.
What is a STEEPLE Analysis?
STEEPLE analysis is a strategic planning tool designed to help organizations evaluate the various external factors influencing their business operations. It expands upon the traditional PESTLE Analysis Template , incorporating Ethical and Legal factors to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the business environment. The seven components of STEEPLE analysis include Social, Technological, Economic, Environmental, Political, Legal, and Ethical factors.
STEEPLE analysis is significant because it helps align business strategies with societal and ethical expectations. By examining factors such as demographics, technological advancements, and legislative changes, businesses can better anticipate changes and adapt more efficiently. This alignment not only enhances an organization’s strategic decision-making but also reinforces its reputation in meeting societal and ethical standards.
When to Use a STEEPLE Analysis
Understanding when to conduct a STEEPLE analysis is crucial for maximizing its effectiveness in strategic planning. This comprehensive tool, which examines Sociopolitical, Technological, Economic, Environmental, Legal, and Ethical factors, is particularly beneficial during moments of significant decision-making. Here are some scenarios where utilizing a STEEPLE analysis is advantageous:
Before Entering New Markets:
When a business considers expansion into new territories, a STEEPLE analysis can illuminate cultural nuances, technological landscapes, economic conditions, political climates, and legal regulations that are vital for successful entry and operations.
Prior to Major Investment Decisions:
Potential investors or stakeholders can leverage the insights obtained from a STEEPLE analysis to assess risks and opportunities. This comprehensive evaluation ensures investments are strategically sound and align with ethical and environmental standards.
During Organizational Changes:
Whether it’s restructuring, launching new products, or implementing significant internal changes, conducting a STEEPLE analysis helps organizations understand external factors that might influence these changes. Insights into legal constraints, political landscapes, or social trends can guide smoother transitions.
Product Development:
For teams focusing on innovation and new product development, the analysis framework provides critical market data and insights into social and technological trends. It helps in shaping products that resonate well with the target audience by aligning with economic and ethical considerations.
Workforce Planning:
As organizations adapt to changing market demands and technological advancements, a STEEPLE analysis helps in workforce planning. Understanding economic trends and educational demographics aids in preparing for future talent needs and creating training programs that cater to evolving business environments.
By integrating STEEPLE analysis into these scenarios, businesses can make informed, data-driven decisions that not only respect the external environment but also enhance their strategic positioning. PESTLE Analysis Example provides further insights and practical examples, extending the application of these frameworks. Similarly, exploring a PEST Analysis Template can assist teams in navigating specific external challenges effectively.
Exploring the Seven Elements of STEEPLE Analysis
STEEPLE analysis is an invaluable strategic planning tool that encompasses seven critical components, each representing distinct external factors affecting business operations and strategies. These components include Social, Technological, Economic, Environmental, Political, Legal, and Ethical factors. Each aspect offers unique insights into how external environments can influence a company’s long-term planning. Let’s dive into each component in detail:
1. Social Factors: Understanding Cultural and Demographic Dynamics
The social dimension of STEEPLE analysis delves into the intricate tapestry of human behavior, cultural trends, and demographic shifts that profoundly impact business operations. In an increasingly interconnected world, understanding social factors is no longer optional but essential for strategic success. Organizations must develop a deep, empathetic understanding of the changing social landscape to effectively connect with their markets, develop relevant products, and anticipate emerging consumer needs.
Demographics: The Changing Human Landscape
Demographics provide the foundational data that underpins social analysis. This includes examining population age structures, cultural compositions, educational attainment, and geographic distribution. For instance, an aging population in developed countries might drive demand for healthcare innovations, while a young, tech-savvy population in emerging markets could create opportunities for digital services and products.
Lifestyle Transformations
Contemporary lifestyles are characterized by rapid change and increasing complexity. The rise of remote work, digital connectivity, wellness consciousness, and flexible career paths fundamentally reshapes consumer expectations and behavior. Businesses must be agile enough to recognize and respond to these shifting lifestyle patterns, whether it’s developing products that support work-life balance or creating services that cater to increasingly personalized consumer experiences.
Evolving Social Values
Social values represent the collective beliefs and principles that guide societal behavior. Today’s consumers are increasingly driven by considerations of sustainability, social justice, diversity, and ethical consumption. Companies that can authentically align with these values – not through superficial marketing, but through genuine organizational commitment – can build deeper, more meaningful connections with their stakeholders.
2. Technological Factors: Navigating the Digital Revolution
Technology has become the primary driver of business transformation, reshaping industries, creating new markets, and rendering traditional business models obsolete. The technological dimension of STEEPLE analysis explores the dynamic landscape of innovation, digital transformation, and research development that continuously redefines competitive boundaries.
Innovation Ecosystem
The modern innovation landscape is characterized by rapid technological convergence, where advances in one domain quickly propagate across multiple sectors. Artificial Intelligence, quantum computing, biotechnology, and other emerging technologies are blurring traditional industry boundaries, creating unprecedented opportunities for those prepared to explore and integrate these innovations.
Digital Transformation Imperative
Digital transformation is no longer a choice but a survival strategy. Organizations must continuously evolve their technological capabilities, embracing cloud computing, AI-driven analytics, Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, and robust cybersecurity measures. The ability to quickly adapt to and leverage new digital technologies can mean the difference between market leadership and obsolescence.
Research and Development Dynamics
R&D represents the lifeblood of technological progress. By examining investment patterns, patent landscapes, and collaborative research ecosystems, businesses can identify emerging technological trends and potential disruptive innovations. Understanding the R&D landscape helps organizations make informed decisions about technological investments and strategic positioning.
3. Economic Factors: Decoding Financial Landscapes and Market Dynamics
Economic factors form the critical backdrop against which all business strategies are developed and executed. In an era of global interconnectedness and rapid economic transformations, organizations must develop a sophisticated understanding of economic forces that can dramatically impact their operational effectiveness, market positioning, and long-term sustainability.
Inflation and Monetary Dynamics
Inflation represents more than just a numerical indicator; it’s a complex economic phenomenon that influences everything from consumer purchasing power to investment strategies. Central bank policies, global economic conditions, and sector-specific pressures converge to create intricate inflationary landscapes. Businesses must develop nuanced approaches to understanding these dynamics, considering how inflation impacts cost structures, pricing strategies, and overall financial planning.
Economic Growth and Market Trends
Economic growth is a multifaceted concept that extends beyond simple GDP measurements. It encompasses sectoral performances, emerging market opportunities, global economic interconnectedness, and the complex interactions between different economic ecosystems. Organizations that can effectively read and interpret these growth patterns can position themselves to capitalize on emerging opportunities and mitigate potential risks.
Labor Market and Employment Landscapes
The modern employment landscape is characterized by unprecedented complexity. Traditional employment models are being disrupted by the gig economy, technological automation, and rapidly changing skill requirements. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for businesses in workforce planning, talent acquisition, and strategic human resource management.
4. Environmental Factors: Sustainability as a Strategic Imperative
Environmental considerations have evolved from peripheral concerns to central strategic considerations for modern organizations. The environmental dimension of STEEPLE analysis explores the complex interplay between business operations, ecological systems, and sustainability imperatives.
Climate Change and Ecological Challenges
Climate change represents a profound global challenge that transcends traditional business boundaries. Organizations must understand how environmental shifts impact their operations, supply chains, and long-term strategic planning. This includes analyzing temperature trends, extreme weather event potentials, and the broader ecological implications of business activities.
Sustainability Practices and Innovation
Sustainability is no longer just a corporate social responsibility initiative but a fundamental business strategy. Circular economy principles, green technology investments, and comprehensive waste reduction strategies are becoming critical differentiators in competitive markets. Businesses that can effectively integrate sustainability into their core operations can create significant value and competitive advantage.
Regulatory Compliance and Environmental Standards
Environmental regulations are becoming increasingly sophisticated and stringent. Organizations must navigate complex compliance landscapes, including emissions trading systems, sustainable reporting requirements, and industry-specific environmental standards. Proactive environmental management can transform potential regulatory challenges into opportunities for innovation and market leadership.
5. Political Factors: Navigating Geopolitical Complexities
Political factors represent the governmental and institutional frameworks that shape business environments. Understanding political dynamics is crucial for organizations seeking to develop robust, adaptive strategies in an increasingly complex global landscape.
Regulatory Environments and Policy Landscapes
Political contexts create the fundamental frameworks within which businesses operate. This includes understanding legislative changes, government policy directions, and the intricate interactions between governmental bodies and private sector entities. Organizations must develop sophisticated political intelligence to navigate these complex environments effectively.
Tax Policy and Fiscal Strategies
Tax policies represent critical strategic considerations for businesses. This encompasses corporate tax rates, international taxation frameworks, investment promotion policies, and the complex interplay between fiscal strategies and business operations. Understanding these dynamics allows organizations to develop more effective financial planning and investment strategies.
Political Stability and Risk Management
Political stability directly impacts business risk profiles. Organizations must develop comprehensive approaches to understanding geopolitical tensions, regulatory shifts, and potential political disruptions that could impact their operations.
6. Legal Factors: Compliance and Strategic Governance
Legal considerations form the critical boundaries within which businesses must operate. The legal dimension of STEEPLE analysis explores the complex regulatory landscapes that govern organizational activities.
Regulatory Compliance Frameworks
Compliance is far more than a box-checking exercise. It represents a fundamental aspect of organizational risk management and strategic governance. This includes understanding labor laws, consumer protection regulations, and the intricate legal frameworks that govern business operations.
Intellectual Property and Innovation Protection
Intellectual property represents a critical strategic asset for modern organizations. Understanding patent landscapes, trademark protections, and innovation rights is crucial for businesses seeking to protect and leverage their intellectual capital.
Legal Risk Management
Effective legal strategy involves proactively managing potential legal risks, understanding emerging legal trends, and developing robust governance frameworks that protect organizational interests while enabling strategic flexibility.
7. Ethical Factors: Building Trust and Organizational Integrity
Ethical considerations have emerged as a critical strategic dimension for modern organizations. The ethical component of STEEPLE analysis explores how businesses can develop strategies that align with broader societal expectations and moral imperatives.
Corporate Social Responsibility
Modern corporate social responsibility extends far beyond traditional philanthropy. It represents a comprehensive approach to creating positive societal impact, aligning organizational objectives with broader human and environmental welfare considerations.
Transparency and Stakeholder Trust
Organizational transparency has become a critical competitive differentiator. Businesses must develop sophisticated approaches to communication, stakeholder engagement, and ethical decision-making that build trust and credibility.
Fair Labor Practices and Human Rights
Ethical business practices now encompass comprehensive approaches to human rights, fair labor practices, and creating inclusive, supportive work environments. Organizations that can effectively integrate these considerations into their operational strategies can create significant competitive advantages.
Helpful Resources
A hierarchical decomposition method that breaks down project deliverables into smaller, more manageable components.
A responsibility assignment framework that defines four key roles in task completion and decision-making processes.
Kanban boards provide real-time visualization of work progress through distinct stages of completion.
Benefits of STEEPLE Analysis for Strategic Planning
Risk Assessment and Adaptability
STEEPLE analysis is an indispensable tool for businesses to comprehensively assess risks by evaluating social, technological, economic, environmental, political, legal, and ethical factors. This broad-spectrum examination enables organizations to proactively identify potential threats and adapt their strategies accordingly, ensuring longevity and resilience in a dynamic market landscape. By anticipating changes, businesses can mitigate risks effectively and seize new opportunities, enhancing their ability to thrive.
For example, a company in the electronics sector might employ STEEPLE analysis to foresee emerging regulations around e-waste, allowing the company to implement recycling initiatives ahead of time, thus reducing compliance risks.
Enhanced Market Awareness
The comprehensive nature of STEEPLE analysis equips businesses with a heightened awareness of market dynamics and evolving consumer expectations. By analyzing trends within each component, organizations can strategize more effectively, catering to demands and positioning themselves competitively. This is particularly beneficial in developing marketing plans and identifying new market niches.
A retail firm, for instance, might use STEEPLE insights to note a rising consumer interest in sustainable products, leading to an expanded eco-friendly product line that aligns with market preferences.
Alignment with Ethical Standards
One of the standout features of STEEPLE analysis is its incorporation of ethical factors, ensuring that businesses adhere to moral principles and societal expectations. By aligning strategies with ethical standards, businesses not only strengthen their reputation but also build trust with stakeholders and consumers.
Consider a cosmetics company that identifies growing regulations on animal testing through STEEPLE analysis. By shifting to cruelty-free alternatives, the company can align with consumer ethics, gaining favor with ethically conscious customers.
Creately enhances the execution of STEEPLE analysis by providing a platform that integrates Strategic Analysis Tools and offers examples for deeper insights. These resources support businesses in mapping out their strategies visually, fostering collaborative strategic planning that ensures all team members are aligned and data-driven decisions are made efficiently. With the aid of features like Data-Driven Decisions and Collaborative Strategic Planning, businesses can significantly enhance their market awareness and align more closely with ethical standards during strategic planning.
How to Conduct a STEEPLE Analysis
Conducting a STEEPLE analysis is a critical undertaking for businesses aiming to understand and adapt to external conditions effectively. This guide provides a structured approach to embark on a thorough STEEPLE analysis, integrating data-driven tools like Creately to optimize the process.
Step-by-Step Guide
1. Set Clear Objectives:
Define goals for your STEEPLE analysis at the outset. Determine whether the focus is on identifying risks, spotting opportunities, or aligning business strategies with external factors. Clear objectives streamline the process and ensure all efforts contribute to actionable outcomes.
Define the Purpose: Determine the primary aim of the analysis. Is it for market entry, risk assessment, or strategy alignment?
Clarify the Scope: Decide whether the analysis will focus on the entire organization, a specific department, or a product line.
Specify Outcomes: Identify the desired outcomes, such as a strategic roadmap, risk mitigation strategies, or a SWOT-like overview.
Engage Stakeholders: Involve relevant stakeholders early to align on goals and ensure buy-in for the process.
2. Gather Relevant Information:
Collect detailed data for each factor in the STEEPLE framework—social, technological, economic, environmental, political, legal, and ethical. Utilize Research Data Analysis Methods to systematically gather insights from diverse sources, ensuring a comprehensive view.
Social: Demographics, cultural trends, consumer behavior, and lifestyle changes.
Technological: Emerging technologies, automation trends, and the state of digital infrastructure.
Economic: Inflation rates, employment trends, market conditions, and purchasing power.
Environmental: Climate change impacts, sustainability trends, and local ecological regulations.
Political: Government policies, trade relations, and geopolitical stability.
Legal: Compliance requirements, intellectual property laws, and industry-specific regulations.
Ethical: Corporate social responsibility (CSR), ethical labor practices, and societal expectations.
Data Collection Methods: Leverage surveys, industry reports, academic research, and internal analytics to compile reliable data.
3. Assess Competitors:
Research your competitors to understand how they respond to similar external factors. This can highlight potential market gaps and competitive advantages. Use tools like Creately’s Business Analysis Tools to compile and compare data efficiently.
Analyze Competitor Strategies: Examine how competitors navigate social, economic, or technological factors.
Identify Market Gaps: Look for underserved market segments or inefficiencies competitors face.
Evaluate Best Practices: Assess strategies that have proven successful in addressing external factors.
Use Business Analysis Tools: Platforms like Creately help visually compare strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT) across competitors.
4. Centralize Information:
Use a collaborative platform such as Creately’s visual canvas to centralize and organize your information. This ensures that all team members can access and contribute to a unified data set, facilitating cohesive analysis and strategy development.
Choose a Collaborative Platform: Use tools like Creately’s visual canvas for seamless data integration and sharing.
Organize by STEEPLE Factors: Create dedicated sections or layers for each factor, ensuring clarity.
Foster Collaboration: Allow team members to contribute real-time insights or feedback.
Maintain Version Control: Use a single source of truth to avoid data duplication or conflicts.
5. Identify Opportunities and Threats:
Analyze the collected data to pinpoint potential opportunities and threats within each STEEPLE category. Visual tools can help map out these elements, making it easier to understand correlations and impacts on strategy.
Opportunities: Identify untapped markets, emerging technologies, or favorable economic conditions.
Threats: Highlight risks such as regulatory changes, economic downturns, or environmental challenges.
Use Visual Tools: Leverage tools like mind maps or correlation diagrams to link factors and visualize their impact.
Conduct Scenario Analysis: Simulate different scenarios to understand potential outcomes and prepare contingency plans.
6. Develop Strategic Plan:
Based on your findings, formulate a strategic plan that addresses identified threats and leverages opportunities. The plan should incorporate data-linked visual frameworks to ensure strategic objectives are clearly mapped out and aligned with real-time data for precise decision-making.
Prioritize Actions: Rank initiatives based on their potential impact and feasibility.
Set Measurable Goals: Define KPIs and timelines to track progress.
Allocate Resources: Ensure the right people, budget, and tools are in place to execute the plan.
Integrate Visual Frameworks: Use data-linked diagrams and workflows for better clarity and alignment.
Monitor and Adjust: Regularly review the plan against real-time data to make necessary adjustments.
By following these steps, businesses can harness the full potential of STEEPLE analysis to foster growth and mitigate risks effectively. Employing visual tools like those offered by Creately not only enhances the analytical process but also facilitates collaborative strategic planning, helping teams achieve targets together and optimize with analysis frameworks for better results.
Difference Between STEEPLE and PESTLE Analysis
When evaluating the external business environment, both STEEPLE and PESTLE analyses offer insightful frameworks. However, it’s crucial to comprehend their distinctions to leverage the appropriate strategy.
| Aspect | STEEPLE Analysis | PESTLE Analysis |
| Scope | Incorporates seven components: Social, Technological, Economic, Environmental, Political, Legal, and Ethical factors. Places a strong emphasis on ethical considerations. | Focuses on six components: Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors. Often employed for understanding macro-environmental influences. |
| Ethical Factors | Explicit inclusion of ethical factors, addressing moral principles in business practices and societal impacts. | Lacks specific evaluation of ethical factors, focusing instead on direct regulatory and environmental influences. |
| Business Alignment | Guides businesses to align strategies with societal expectations and legal responsibilities efficiently. | Helps identify and adapt to external regulatory changes and economic trends. |
| Use Cases | Ideal for companies emphasizing corporate social responsibility and ethical governance. | Commonly used in market entry strategies and compliance assessments. |
In terms of application, STEEPLE analysis extends its value by addressing ethical dimensions, which can be a game-changer for businesses prioritizing comprehensive corporate responsibility. On the other hand, PESTLE analysis remains a steadfast choice for those seeking a foundational approach to understanding the macro-environmental factors.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid When Conducting a STEEPLE Analysis
Engaging in a STEEPLE analysis can be transformative, but missteps can lead to skewed results. Here are some pitfalls to watch out for and strategies to bypass them, ensuring a robust analysis:
Avoid Overgeneralizing Data
- Gathering data from a limited set of sources often results in a superficial understanding. Supplement your primary findings with broader perspectives to form a truly comprehensive view.
Focusing Exclusively on One Factor
- Each element in the STEEPLE analysis, from social to ethical factors, plays an integral role in shaping your strategic insights. Ensure a balanced analysis by evenly distributing focus across all components.
Ignoring the Iterative Nature
- Analysis isn’t a one-time event. Continually refine your assessment as new data and trends surface, keeping your business strategy agile and responsive.
Lack of Collaborative Efforts
- Relying on a single viewpoint can limit your insights. Draw upon diverse perspectives within your team to enrich your analysis with varied expertise and viewpoints.
For effective strategic planning, consider using tools like the SWOT Analysis Maker that enable collaboration and support a detailed examination of external and internal factors impacting your business.
How Steeple Analysis is Used Across Industries
Automotive Industry: Companies like Tesla have utilized STEEPLE analysis to strategize their push towards electric vehicles. Recognizing social trends favoring sustainability, Tesla’s shift aligns with societal values and technological advancements, propelling them forward in the competitive market.
Food and Beverage Sector: PepsiCo employed STEEPLE analysis to address health-conscious social trends and economic factors. They diversified their product lines to include healthier options, aligning with consumer preferences while considering economic conditions and regulatory compliance.
Technology Firms: Giants like Apple often conduct STEEPLE analyses to gauge economic fluctuations, technological trends, and legal regulations. This helps them adapt product offerings and compliance strategies, allowing them to maintain an innovative edge.
Renewable Energy: By using the framework, companies in the renewable sector assess social and political support for sustainability, tailoring their operations to align with government incentives and societal demands.
Healthcare Institutions: Hospitals and healthcare providers analyze factors such as demographic changes and technological innovations to improve patient care and streamline operations, ensuring better service delivery.
These applications demonstrate the versatility of STEEPLE analysis in adapting to market dynamics, predicting environmental shifts, and sustaining competitive advantage. With its robust integration of ethical considerations, companies can also navigate modern challenges more responsibly. For those seeking practical templates to initiate their analysis, the STP Model Template provides a structured approach to leveraging these insights effectively.
Mastering STEEPLE Analysis can significantly enhance strategic insights and decision-making within your organization. By incorporating this holistic approach, businesses can better align their strategies with external factors, ensuring they remain adaptive and competitive. This comprehensive tool evaluates social, technological, economic, environmental, political, legal, and ethical factors, providing a panoramic view of the external forces at play.
Utilizing STEEPLE Analysis with platforms like Creately streamlines this process through visual mapping and real-time data integration. As businesses face unpredictable markets and evolving societal values, incorporating tools like the STP Model can further enrich strategic planning by enhancing understanding of customer segmentation and positioning.
Sources
“How STEEPLE Analysis Informs Design Strategy.” Delve, 2022, www.delve.com/insights/how-steeple-analysis-informs-design-strategy.
Jim Makos. “Difference between STEEP and STEEPLE Analysis.” 1 April. 2024, www.pestleanalysis.com/steep-and-steeple-analysis/.
“STEEPLE Analysis.” Mr. Dachpian’s MYP Humanities, DP Economics & DP Business Management Page, www.dachpian.weebly.com/steeple-analysis.html.